There are five main types of fire extinguishers: water, foam, dry powder, CO2, and wet chemical. To adhere to regulations, the correct fire extinguisher (paying attention to its size and weight) must be located in the right place in your building. Fire risk depends on the type of fuel that may cause a fire in a given area.
Here's an overview of the five types of fire extinguishers and their uses.
What are the classes of fire?
All fires are not made equal. Different classes of fire are governed by what type of material the fire starts with. Understanding the type of fire that may arise in your building is a prerequisite to finding the right fire extinguisher. You will also need the right size and weight of fire extinguishers and put them in the correct place.
Class A fires
Combustible materials, including flammable solids, such as wood, paper, and textiles.
Class B fires
Flammable liquids, including petrol, paint, and spirits.
Class C fires
Flammable gases, including propane and butane.
Class D fires
Flammable metals, including chemicals such as magnesium, lithium, and potassium.
Class E fires
Electrical equipment, including computers and photocopiers.
Class F fires
Cooking oils, including olive oil and butter.
What are the five main types of fire extinguishers?
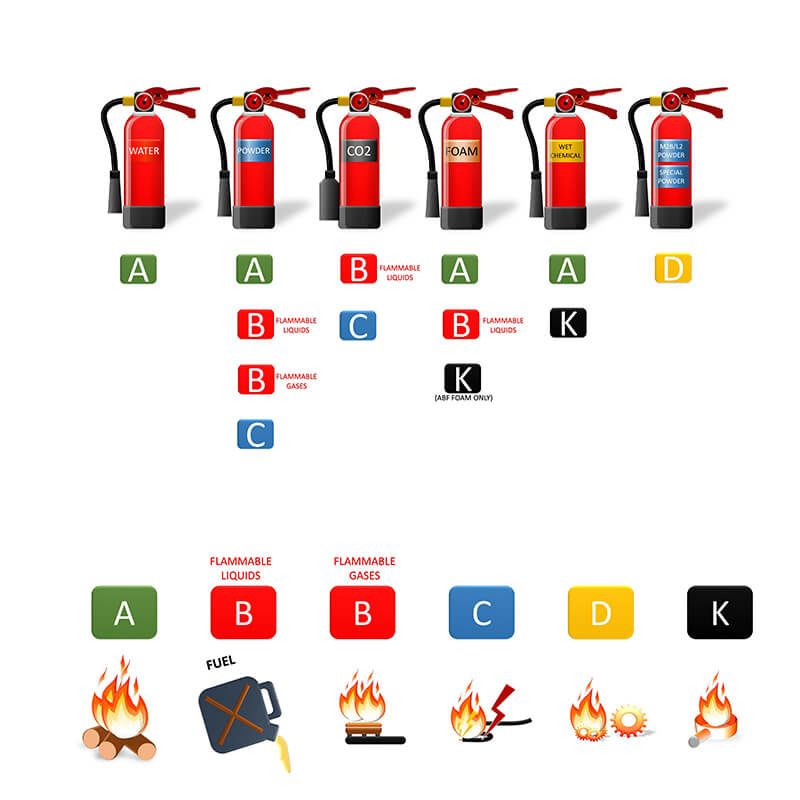
1. Water fire extinguishers for Class A fires
Standard water fire extinguishers can only be used on fires involving flammable solids. However, they are still useful for most buildings, including warehouses and storage facilities. They are available in 3, 6, and 9-litre sizes.
When the fire extinguishers are directed at flames, the water's extreme cooling effect lowers the temperature of the material on fire, making it impossible for the fire to burn.
Water fire extinguishers have a white-coloured label stating ‘Water’. They should be identified by a nearby extinguisher ID sign fixed nearby stating ‘Water Extinguisher’.
What are water fire extinguishers used for?
Water fire extinguishers are ubiquitous as they are 'traditional fire extinguishers'; however, current guidelines often recommend foam extinguishers as they can extinguish both Class A and B fires.
Regardless, they are still useful for areas that contain a large amount of combustible material, such as warehouses, storage units, paper mills, and textile factories.
They are also helpful in domestic environments alongside CO2 extinguishers, so the most likely fire types can be covered.
Do not use water fire extinguishers for:
- Electrical fires as doing so can lead to electrocution
- Cooking fires, such as chip pan fires (Class F fires)
- Fires involving flammable gases, such as methane and butane (Class C fires)
- Fires involving flammable liquids, such as petrol and paint (Class B fires)
2. Foam fire extinguishers
Foam extinguishers, also known as AFFF foam fire extinguishers, are generally used for fires involving flammable solids and liquids. They are available in 2, 3, 6, and 9-litre sizes—although 6 litre is the most common.
They can be identified with a cream–coloured label printed on the body stating ‘Foam’. Also, an ID sign should be placed near them stating ‘Foam Extinguisher’.
Foam fire extinguishers work in two ways. First, they are water-based so they lower the temperature of the fire. Second, they extinguish flames with their aqueous film forming foam (AFFF), which smothers the fire, preventing it from reigniting. The foam can be used on flammable liquids as it places a barrier between the liquid and the flames.
Foam fire extinguishers are ideal for places with multiple fire risks, including hotels, offices, garages, and factories. Most buildings can benefit from having a foam fire extinguisher.
What are foam fire extinguishers used for?
- Fires involving flammable solids, including paper, wood, and textiles (Class A fires)
- Fires involving some flammable liquids, including petrol, diesel, and paint (Class B fires)
Do not use foam fire extinguishers for:
- Cooking fires involving oil and grease (Class F fires)
- Fires involving flammable gases (Class C fires)
3. Dry powder fire extinguishers
Dry powder fire extinguishers (also known as dry chemical fire extinguishers and multi-purpose fire extinguishers) are incredibly versatile and can be used for almost every kind of fire. However, they aren’t recommended for use in enclosed spaces. The extinguishers come in 1, 2, 3, 6, and 9 kg sizes.
Dry powder fire extinguishers have a blue label stating powder, and they can be identified by an ID tag saying Powder Extinguisher.
Dry powder fire extinguishers work by smothering fires; they place a barrier between the source of oxygen and the fuel, so they can be used on most types of fires. They suppress fires very quickly; however, they do not cool the fire, so it could reignite. Specialist dry powder fire extinguishers work on flammable metals.
Dry powder fire extinguishers are suitable indoors and outdoors as they can be used with several different types of fire, including chemicals, fuel, or vehicles.
- Garage forecourts
- Large, commercial boiler rooms
- Flammable liquid storage facilities
- Large workshops
- Fuel tankers and other vehicles
What are dry powder fire extinguishers used for?
- Fires involving flammable solids (Class A fires)
- Fires involving flammable liquids (Class B fires)
- Fires involving combustible gases (Class C fires)
- Electrical fires involving some electrical items under 1000v
For electrical fires, it is also useful to have CO2 extinguishers, especially in kitchens or if there are electric heaters around.
- Specialist dry powder extinguishers work for flammable metals
Do not use dry powder fire extinguishers for:
- Fires involving cooking oil (Class F fires)
- Fires involving electrical items over 1000v
- Fires in enclosed spaces
4.CO2 fire extinguishers
CO2 fire extinguishers (also known as carbon dioxide fire extinguishers) are mainly used for electrical fires. Guidelines advise that they are paired with foam extinguishers.
CO2 fire extinguishers can be identified by a black label saying CO2. They have a distinctive black nozzle and should have an ID tag saying CO2 Extinguisher.
CO2 fire extinguishers discharge carbon dioxide, which is stored as a liquid and converts to a gas when released. As the gas is released at speed, the fire extinguishers should not be used with fires involving cooking oil as they may spread the fire.
CO2 fire extinguishers do not cool fires; instead, they replace oxygen with carbon dioxide, thus removing the fuel. For this reason, they are very effective with electrical fires. CO2 fire extinguishers are particularly recommended for places with a lot of electrical equipment, including offices, schools, and hospitals, where they should be paired with foam extinguishers.
CO2 fire extinguishers come in 2 and 5-kg sizes.
What are CO2 fire extinguishers used for?
- Fires involving equipment such as computers, or generators (‘electrical’ fires)
- Fires involving some flammable liquids, such as petrol, diesel, and paint (‘class B’ fires)
Do not use CO2 extinguishers for:
- Fires involving oil and grease (Class F fires)
Wet chemical fire extinguishers
Wet chemical fire extinguishers (also known as Class F fire extinguishers) are the only extinguisher that can safely be used for fires involving cooking oil; therefore, they are essential in professional kitchens and fast food restaurants.
Wet chemical fire extinguishers have a yellow label saying ‘Wet Chemical’. They also have a longer hose than the standard extinguishers and have an ID tag saying ‘Wet Chemical Extinguisher’.
Potassium is the chemical component of the fire extinguishers, and the chemical is gently sprayed out to not burn the fats and oils. It creates a film over the grease to suffocate the fire.
Whilst they are excellent and extinguishing grease fires, they can produce toxic fumes, so areas must be ventilated.
Wet chemical fire extinguishers are available in 2, 3, and 6-litre sizes.
What are wet chemical fire extinguishers used for?
- Fires involving cooking oils and fats (Class F fires)
- Fires involving flammable solids (Class A fires)
Some wet chemical fire extinguishers can also be used for fires involving flammable liquids; however, the exact use will be written on the label.
Do not use wet chemical fire extinguishers for:
- Fires involving flammable liquids (‘class B’ fires) UNLESS they are specifically cleared for this use
- Fires involving combustible gases, such as methane and butane ('class C' fires)
- Electrical fires
Conclusion
To protect your business and ensure compliance with UK fire safety regulations, you must have the proper fire extinguisher installed correctly. Once your fire extinguishers are installed, they must also be commissioned by law—meaning that they have been fully checked and approved.




 Previous Blog
Previous Blog

Comments.